Nancy Laboratory for Rabies and Wildlife
Laboratory Director: David Fenard
Deputy Director: Franck Boué
Address: Bâtiment H - Technopôle Agricole et Vétérinaire – Domaine de Pixérécourt - CS 40009 - 54220 MALZEVILLE, France
Email: contact.lrfsn@anses.fr
Team: 40 people, spread out across two units and an experimental station
The laboratory's missions
The Nancy Laboratory for Rabies and Wildlife studies pathogens circulating in wildlife, in particular zoonotic ones (able to be transmitted from animals to humans), with an approach that focuses on selected pathogens or animal species. This vast topic is studied according to three strands: surveillance, study of eco-epidemiology, and prevention and control. These strands feed into each other, and some projects may be at the intersection of several strands.
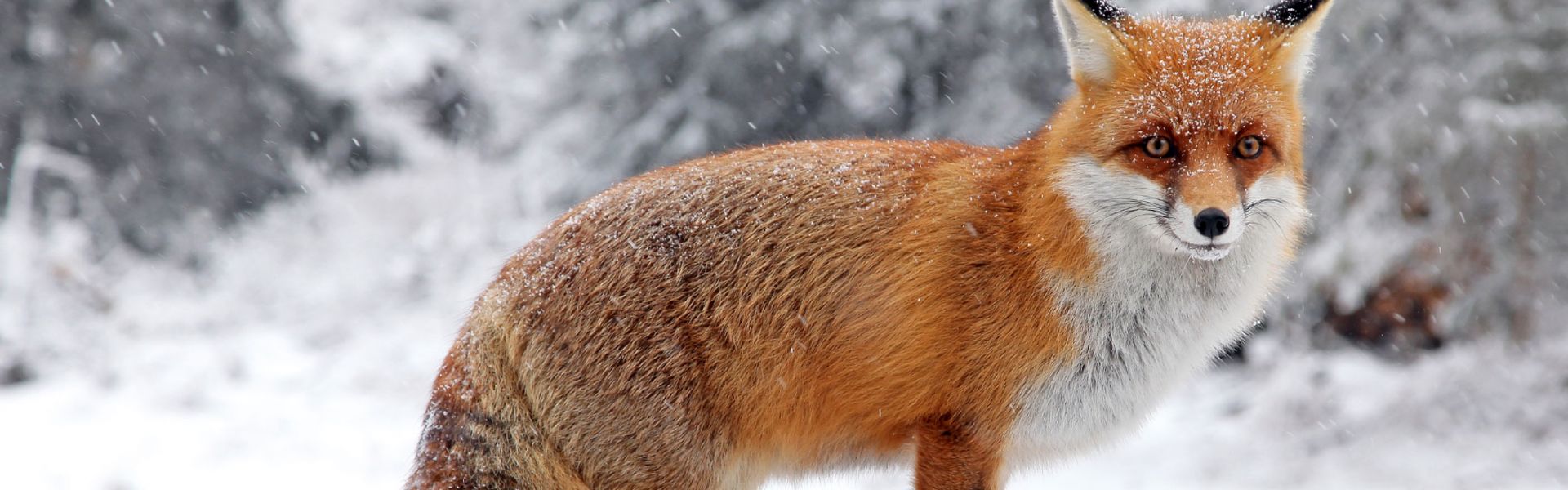
A significant part of the laboratory's work focuses on animal rabies. At the national level, the objective is to maintain France's rabies-free status for non-flying mammals (such as dogs and foxes) and to monitor bats for lyssaviruses, a group of viruses that includes rabies. At the international level, the laboratory provides its expertise and takes part in rabies elimination programmes around the world.
It also specialises in the study of other zoonotic agents circulating in wildlife, at the interface with humans, and domestic and farm animals. In particular, it works on parasites of the genus Echinococcus sp. responsible for cystic echinococcosis or hydatid disease; on the bacterium Mycobacterium bovis responsible for bovine tuberculosis; and on tick-borne encephalitis virus, orthohantaviruses and coronaviruses. Its tasks on these pathogens include surveillance, research and/or reference activities.
To know more about the Laboratory
>> See the leaflet (PDF)
David Fenard appointed Director of ANSES's Laboratory for Rabies and Wildlife
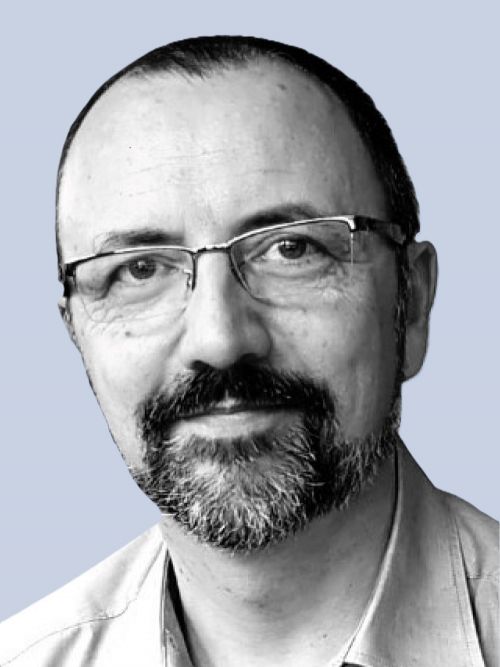

Since 2 February 2026, David Fenard has been the new Director of ANSES's Laboratory for Rabies and Wildlife, located near Nancy. A virologist by training, he is now responsible for this laboratory specialising in the study of pathogens circulating in wildlife.
The laboratory's units
The laboratory's scientific activities are shared between two units, the Lyssavirus Unit and the Surveillance and Eco-epidemiology of Wildlife Unit, as well as with an experimental station devoted to wild carnivores:
Experimental station
The experimental station supports the laboratory units but also carries out its own projects. It capitalises on its expertise and technical strengths on wild carnivores and rodents to explore the role of wildlife in zoonoses and the transmission of pathogens to domestic animals. In particular, it works on the mechanisms of transmission, the crossing of the species barrier and the immune response of wild animal species.
Partnerships
The laboratory is involved in multiple partnerships that change according to the topics. Cooperation ranges from regional to international.
Regional partners
- National Reference Centre for Borrelia - Strasbourg university hospital
- Permanent centre for initiatives on the environment, Champenoux
- Greater Nancy metropolitan area
National partners
- Naturalist associations (French society for the study and protection of mammals, chiropterologists, Lorraine mammal study group etc.);
- French Agricultural Research Centre for International Development (CIRAD)
- National Reference Center (CNR) for measles, mumps and rubella viruses - Caen University Hospital
- Other National reference centres for the pathogens studied
- Directorate General for Food (DGAL)
- Directorate General for Health (DGS)
- Veterinary schools (ENVA, ENVT, Oniris, VetAgro sup)
- National and departmental hunters' federations
- French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and the Environment (INRAE)
- Departmental testing laboratories
- French Biodiversity Agency (OFB)
- Universities
European and international partners
- Animal and Plant Health Agency (APHA), UK
- Public Health England (UKHSA), UK
- Agricultural and Food Development Authority (TEAGASC), Ireland
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
- Animal Health Research Centre (CRESA), Spain
- European Commission (EC)
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines (EDQM)
- National Veterinary Research Institute (PIWET), Poland
- National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM), Netherlands
- Institut Pasteur in Tunis, Tunisia
- Friedrich Loeffler Federal Institute for Animal Health Research (FLI), Germany
- Taiwan Animal Health Research Institute (AHRI)
- European Union Reference Laboratory (EURL) for parasitology (Italian National Institute of Health, ISS)
- National Office of Food Safety (ONSSA), Morocco
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
- European network of national reference laboratories for rabies
- European and international network of official rabies serology laboratories
- Networks of official rabies serology laboratories
- Universities of Barcelona and León (Spain), Tartu (Estonia), Iasi (Romania), Surrey (UK), Georgia (USA), Ulaanbaatar (Mongolia) and Monastir (Tunisia)